GUIs mit Swing
import javax.swing.*;
public class LabelFrame1 { public static void main(String[] args) { JFrame frame = new JFrame(); frame.setTitle("Swing frame with label"); frame.add(new JLabel("Hello!")); frame.setSize(300, 150); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }}Methoden von Top-Level-Containern
JFrame, JWindow und JDialog
import javax.swing.*;
setTitle(String s); // Title
add(Component comp); // Füge Komponente zum Container hinzu
setSize(int width, int height);
pack(); // Fenstergröße wird an die bevorzugte Größe und das Layout der Komponenten angepasst
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.DO_NOTHING_ON_CLOSE);setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.HIDE_ON_CLOSE);setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setVisible(boolean b); // Macht das Fenster sichtbar
dispose(); // Gibt alle systemeigenen Ressourcen des Fensters freiLayoutmanager
FlowLayout
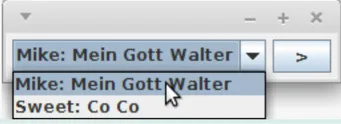
Ordnet Komponenten zeilenweise von links nach rechts an
import java.awt.*;import javax.swing.*;public class FlowLayoutDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { JFrame f = new JFrame(); f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
JComboBox choice = new JComboBox(); choice.addItem("Mike: Mein Gott Walter"); choice.addItem("Sweet: Co Co");
f.add(choice); f.add(new JButton(">")); f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); f.pack(); f.setVisible(true); }}BoxLayout
Ordnet Komponenten horizontal oder vertikal an
GridLayout
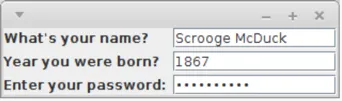
Setzt Komponenten in ein Raster, wobei jedes Element die gleichen Ausmaße besitzt
import java.awt.*;import java.text.*;import javax.swing.*;public class GridLayoutDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { JFrame f = new JFrame(); f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); f.setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 2, 6, 3));
f.add(new JLabel("What's your name?")); f.add(new JTextField()); f.add(new JLabel("Year you were born?")); f.add(new JFormattedTextField(NumberFormat.getIntegerInstance())); f.add(new JLabel("Enter your password:")); f.add(new JPasswordField());
f.pack(); f.setVisible(true); }}BorderLayout
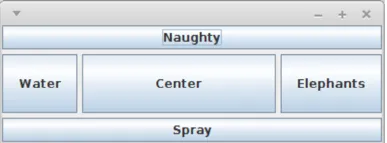
Setzt Komponenten in vier Himmelsrichtungen oder in der Mitte
import java.awt.*;import javax.swing.*;public class BorderLayoutDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { JFrame f = new JFrame(); f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); f.setLayout(new BorderLayout(5, 5));
f.add(new JButton("Naughty"), BorderLayout.NORTH); f.add(new JButton("Elephants"), BorderLayout.EAST); f.add(new JButton("Spray"), BorderLayout.SOUTH); f.add(new JButton("Water"), BorderLayout.WEST); f.add(new JButton("Center"));
f.setSize(400, 150); f.setVisible(true); }}GridBagLayout
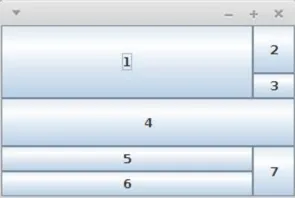
Sehr flexibler Manager als Erweiterung von GridLayout
import java.awt.*;import javax.swing.*;public class GridBagLayoutDemo { private static void addComponent(Container cont, Component c, int x, int y, int width, int height, double weightx, double weighty) { GridBagConstraints gbc = new GridBagConstraints(); gbc.fill = GridBagConstraints.BOTH; gbc.gridx = x; gbc.gridy = y; gbc.gridwidth = width; gbc.gridheight = height; gbc.weightx = weightx; gbc.weighty = weighty; cont.add(c, gbc); } public static void main(String[] args) { JFrame f = new JFrame(); f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); Container c = f.getContentPane(); c.setLayout( new GridBagLayout() ); // x y w h wx wy addComponent(c, new JButton("1"), 0, 0, 2, 2, 1.0, 1.0); addComponent(c, new JButton("2"), 2, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1.0); addComponent(c, new JButton("3"), 2, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0); addComponent(c, new JButton("4"), 0, 2, 3, 1, 0, 1.0); addComponent(c, new JButton("5"), 0, 3, 2, 1, 0, 0); addComponent(c, new JButton("6"), 0, 4, 2, 1, 0, 0); addComponent(c, new JButton("7"), 2, 3, 1, 2, 0, 0); f.setSize(300, 200); f.setVisible(true); }}CardLayout
Verwaltet Komponenten wie auf einem Stapel, von dem nur einer sichtbar ist.
SpringLayout
Berücksichtigt Abhängigkeiten der Kanten vom Komponenten
GroupLayout
Manche GUI-Builder verwenden dieses Layout, kommt aber häufig mit eigenem Layoutmanagern.
NullLayout
Zur absoluten Positionierung
Beispiel eines geschachtelten Layouts
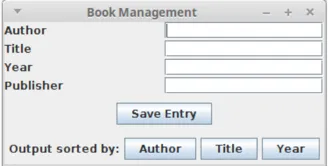
import java.awt.*;import javax.swing.*;
public class BookManagement { public BookManagement() { JFrame jf = new JFrame("Book Management"); jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); jf.setLayout(new BorderLayout(5, 5)); JPanel top = new JPanel(); top.setLayout(new GridLayout(4, 2, 2, 2));
top.add(new JLabel("Author")); top.add(new JTextField(""));
top.add(new JLabel("Title")); top.add(new JTextField(""));
top.add(new JLabel("Year")); top.add(new JTextField(""));
top.add(new JLabel("Publisher")); top.add(new JTextField(""));
jf.add(top, BorderLayout.NORTH);
JPanel mid = new JPanel(); mid.add(new JButton("Save Entry")); jf.add(mid, BorderLayout.CENTER);
JPanel bot = new JPanel(); bot.setLayout(new FlowLayout()); bot.add(new JLabel("Output sorted by:")); bot.add(new JButton("Author")); bot.add(new JButton("Title")); bot.add(new JButton("Year"));
jf.add(bot, BorderLayout.SOUTH); jf.pack(); jf.setVisible(true); }
public static void main(String[] args) { new BookManagement(); }}Standarddialoge mit JOptionPane
// Message dialogJOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "May the force be with you!");
// Input dialogJOptionPane.showInputDialog("Please enter a number");
// Confirm dialogJOptionPane.showConfirmDialog(null, "Are you ok?");
// Select dialogString[] options = {"to be", "not to be", "dont know"};String selection = (String) JOptionPane.showInputDialog(null, "Hamlet", "To be or not to be?", JOptionPane.Question_Message, null, options, options[1]);System.out.println("Chosen: " + selection);Action Listener für Buttons
JButton b = new JButton("Click me!");b.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { System.out.println("Button clicked!"); }});Radio Buttons
JRadioButton rb1 = new JRadioButton("Option 1");JRadioButton rb2 = new JRadioButton("Option 2");ButtonGroup bg = new ButtonGroup();bg.add(rb1);bg.add(rb2);Checkboxes
JCheckBox cb1 = new JCheckBox("Option 1");JCheckBox cb2 = new JCheckBox("Option 2");
if (cb1.isSelected()) { System.out.println("Option 1 selected");}Inputfelder
JTextField tf = new JTextField(20);JPasswordField pf = new JPasswordField(20);
String text = tf.getText();char[] password = pf.getPassword();Listen
String[] items = {"Item 1", "Item 2", "Item 3"};JList<String> list = new JList<>(items);
// Get selected itemString selected = list.getSelectedValue();
// ScrollpaneJScrollPane sp = new JScrollPane(list);
// Add to frameframe.add(sp);
// Add listenerlist.addListSelectionListener(new ListSelectionListener() { public void valueChanged(ListSelectionEvent e) { System.out.println("Selected: " + list.getSelectedValue()); }});Inhalt aktualisieren
Um Inhalt zu aktualisieren, kann das entsprechende Element entfernt und neu hinzugefügt werden.
// Panel erzeugenJPanel panel = new JPanel();
// initiale Anzeige des Inhaltscontent();
// Hinzufügen zum JFramejframe.add(panel);
// Methode zum Aktualisieren des Inhaltspublic void content() { panel.removeAll(); panel.add(new JLabel("New content")); panel.revalidate();}